While learning about various cryptocurrency projects, you’ve probably come across the term Hard Fork, but you might not fully understand it. Today, invest286.com will help you understand exactly what a Hard Fork is in blockchain, why Hard Forks occur, and how they work.
Contents
- 1 What is a Hard Fork in blockchain?
What is a Hard Fork in blockchain?
What is a Hard Fork?
Blockchain technology was created to ensure that data storage is immutable and unchangeable. However, during its operation, issues arise that lead to differing opinions within the community or the desire to upgrade the blockchain for better performance, thus leading to Hard Forks.
A Hard Fork requires all nodes or users to upgrade to the latest version of the protocol software.

What happens to cryptocurrency after a Hard Fork?
When a Hard Fork occurs, the related cryptocurrency will split into two versions: the original and the new one. Holders of the original cryptocurrency may receive an equivalent amount of new coins or a ratio thereof. Usually, both coins are accepted by the community, but one tends to dominate.
Although it may seem like you will get an additional new coin alongside the old one, usually the price of one of the cryptocurrencies will be much lower than the other, so the total value remains similar despite having more coins.
Example of Ethereum’s Hard Fork
In June 2016, a hack occurred on Ethereum, resulting in the theft of approximately 50 million USD from investors. This hack took place at Ethereum blockchain block 1,920,000, leading to two divergent opinions.
- 85% wanted to reverse the Ethereum blockchain to before the hack to retrieve the stolen funds from the hacker.
- The remaining 15% did not want this because their viewpoint was to “maintain a 100% immutable ledger” as per the original purpose of creating the blockchain.
=> As a result, in July 2016, Ethereum’s blockchain underwent a hard fork, splitting Ethereum’s blockchain into two different blockchains. The new blockchain (as per the majority 85%) retained the name Ethereum (ETH) as it is known today, while the old blockchain was renamed to Ethereum Classic (ETC).
Currently, Ethereum (ETH) is priced at $ 1,589.96 while Ethereum Classic (ETC) is only priced at $ 15.45, a significant disparity following Ethereum’s hard fork.
How does a Hard Fork work?
A Hard Fork in blockchain can occur with any cryptocurrency project, not just Bitcoin. The reason is that blockchain and cryptocurrencies fundamentally operate the same way regardless of the platform.
Since the miners in a blockchain set the rules for data movement in the network, a hard fork introduces new rules that miners need to understand.
However, all miners need to agree on the new rules and what constitutes a valid block in the chain. Therefore, when you want to change these rules, you need to “fork” — similar to a fork in the road — to indicate that there has been a change or redirection in the protocol. Subsequently, developers can update all the software to reflect the new rules.
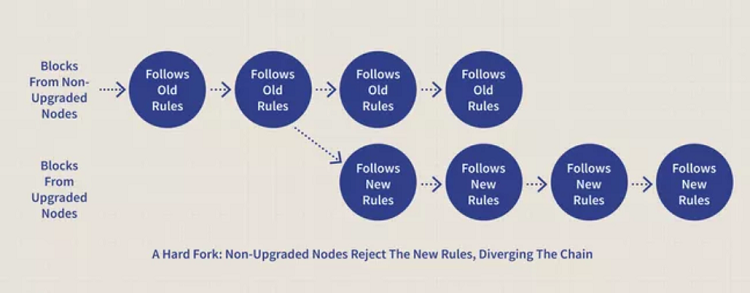
Why do Hard Forks occur?
There are several main reasons for hard forking a blockchain:
-
Differences of opinion on a particular issue within the blockchain community, leading them to split the blockchain into two separate paths.
-
Discovery of security issues in the blockchain and conducting a hard fork to fix these security flaws.
-
Reversing transactions as Ethereum did to prevent attacks and return funds to investors.
-
Adding new functions to the blockchain, upgrading the blockchain to help it operate better and adapt to the current needs of the cryptocurrency industry. For example, if the original blockchain does not support smart contracts or NFTs, the development team may decide to upgrade the blockchain and conduct a hard fork.
How do Hard Forks and Soft Forks differ?

Unlike a Hard Fork, a Soft fork allows new blockchain nodes to communicate with old blockchain nodes and vice versa. This means that, while updates are made, there is no need to create an entirely new blockchain.
As old nodes can still interact with these updates, a soft fork does not require approval from miners and does not cause controversy.
Soft forks typically do not solve major functionality or security issues because the blockchain does not undergo sufficient foundational changes to address the situation.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a Hard Fork?
Notable blockchain hard forks
Ethereum Hard Fork
As mentioned earlier, the most notable Ethereum Hard Fork occurred in 2016, resulting in the formation of Ethereum Classic.
Bitcoin Cash Hard Fork
However, currently, Bitcoin is priced at $ 84,465.63, while Bitcoin Cash is priced at only $ 335.58.
Apart from forking Bitcoin into Bitcoin Cash, there are many other Bitcoin forks with different features. You can read more at: What is a Bitcoin Fork? The most famous Bitcoin Forks in history
Terra (LUNA) Hard Fork
The LUNA – UST crash on May 11, 2022, which led to UST’s inability to maintain a 1:1 peg with the USD, resulted in billions of dollars in investor losses. This event caused a significant loss of confidence in Terra within the cryptocurrency community and triggered a massive sell-off in the market, especially in DeFi.
Subsequently, Terra conducted a hard fork of LUNA into Luna Classic (LUNC) and Terra (LUNA) in an attempt to revive the Terra (LUNA) ecosystem by Do Kwon.
However, due to the loss of investor confidence after the crash, the value of both LUNC and the new LUNA could not return to their former glory. The future of Terra – once a top 20 global market cap currency – remains uncertain. However, it is difficult for Terra to return to its former status due to the lost investor confidence.
Cardano Hard Fork Vasil

The eagerly anticipated Cardano Hard Fork Vasil is expected to significantly boost Dapp development on Cardano.
A notable feature of the Vasil hard fork is the introduction of pipelining, which will enhance block propagation for better scaling. Additionally, it includes several features, such as enhancements to CIP 31, 32, and 33. The Cardano Hard Fork Vasil was completed on September 22nd, right after the Ethereum update “The Merge” took place.
Through this, we hope you now understand what a Hard Fork is in blockchain, as well as the advantages and disadvantages following a Hard Fork. If you have any further questions, feel free to leave a comment to get an answer within 24 hours.


























