If you’re exploring the cryptocurrency market, you’ve likely come across Bitcoin and several of its “variants” such as Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin SV, and others. These are commonly known as Bitcoin Forks. But what exactly is a Bitcoin Fork, and how does it differ from the regular Bitcoin? Let’s delve into the details of Bitcoin Forks and some of the most famous Bitcoin Forks that exist today.
Contents
What is a Bitcoin Fork? What is a Hard Fork?
What is a Bitcoin Fork?
Before we dive into what a Bitcoin Fork is, let’s briefly discuss the concept of a “Fork.”
While ‘Fork’ literally translates to “fork” as in the eating utensil, in the cryptocurrency market, it pertains to blockchain technology.
A Fork represents a change in the blockchain’s protocol that can render a previously valid or invalid block as the opposite. This means a Fork can occur at any moment in the blockchain’s life.
A Bitcoin Fork is essentially the creation of a new chain (block) when the community fails to reach a consensus on the future state of the Bitcoin blockchain. To put it simply, a Bitcoin Fork involves creating a separate copy of the Bitcoin blockchain and implementing changes to it.
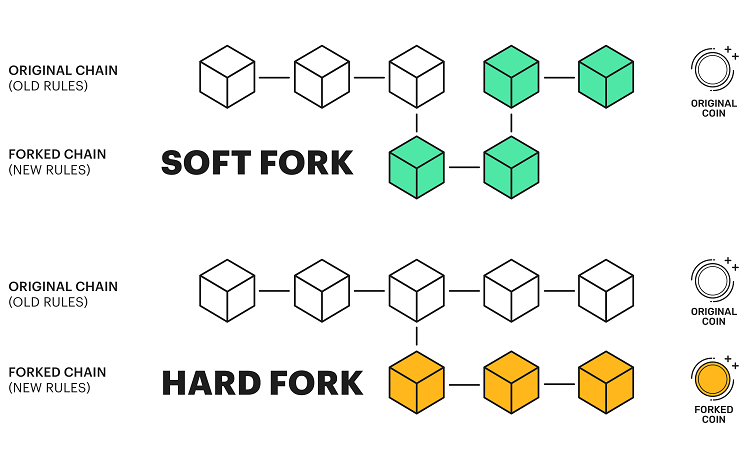
In general, there are two types of Bitcoin forks: “soft fork” and “hard fork”.
What is the purpose of a Bitcoin Fork?
A Bitcoin Fork is conducted when a community (comprising coin holders, miners, etc.) is dissatisfied with certain aspects of Bitcoin. They seek to improve and amend the system to create a better version.
A fork might also occur if a cryptocurrency is under attack (as in the case of Ethereum) or due to disagreements within the coin holder community (as with Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash).
A fork represents a “crossroads,” indicating that there has been a change or a shift in the network’s protocol. Consequently, programmers need to update their software and recreate the content so that the new cryptocurrency accurately reflects the new rules.
How are Soft Fork and Hard Fork different?
Once you understand what a Bitcoin Fork is, you probably know that there are two types of forks: Bitcoin Soft Fork and Bitcoin Hard Fork.
What is a Soft Fork?
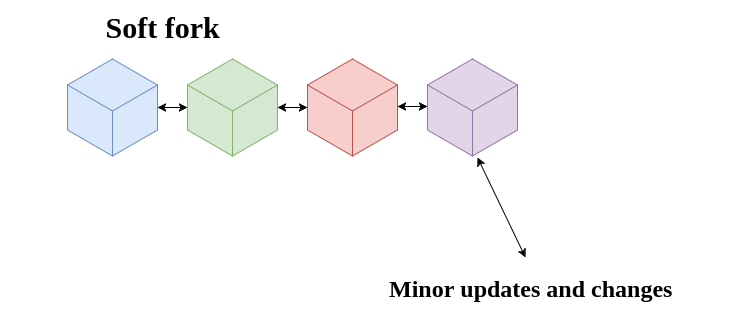
A soft fork is a backwards-compatible method of upgrading a blockchain. To put it simply, a soft fork is like a software upgrade that is backwards compatible with older software versions. A soft fork does not require any nodes within the network to upgrade or maintain consensus. This is because all blocks found in the soft fork blockchain adhere to both the new and the old consensus rules, not just the old ones.
What is a Hard Fork?
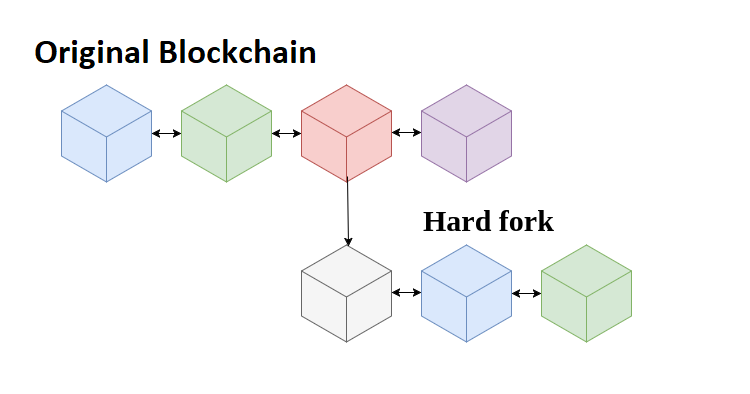
A hard fork is a permanent divergence from the previous versions of the blockchain, and as such, it is not compatible with the older network. Therefore, all participants in the network must upgrade to the newer version of the software to continue verifying and validating new transaction blocks.
A hard fork differs from a soft fork in that it creates a new blockchain. When a hard fork is successful, two blockchains will coexist in parallel.
Note that if you own a cryptocurrency and it undergoes a hard fork, you will automatically receive an additional amount of the new crypto corresponding to your original holdings, while your original quantity of crypto remains unchanged.
If you are a miner and want to mine, you will have to choose one of the two blockchains to work on.
Fundamentally, both Hard Forks and Soft Forks are similar in that they are modifications built upon the old blockchain. However, a Hard Fork creates two parallel blockchains, while a Soft Fork only results in one blockchain.
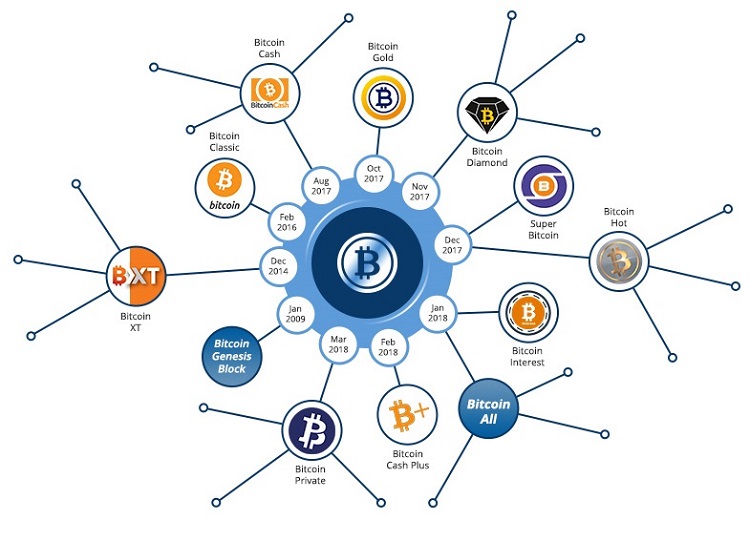
The most famous Bitcoin Hard Forks to date
In the history of cryptocurrency, there have been numerous Bitcoin soft and hard forks. Some of these have led to the creation of new coins that have established a presence in the market, while others have faded away due to a lack of community support.
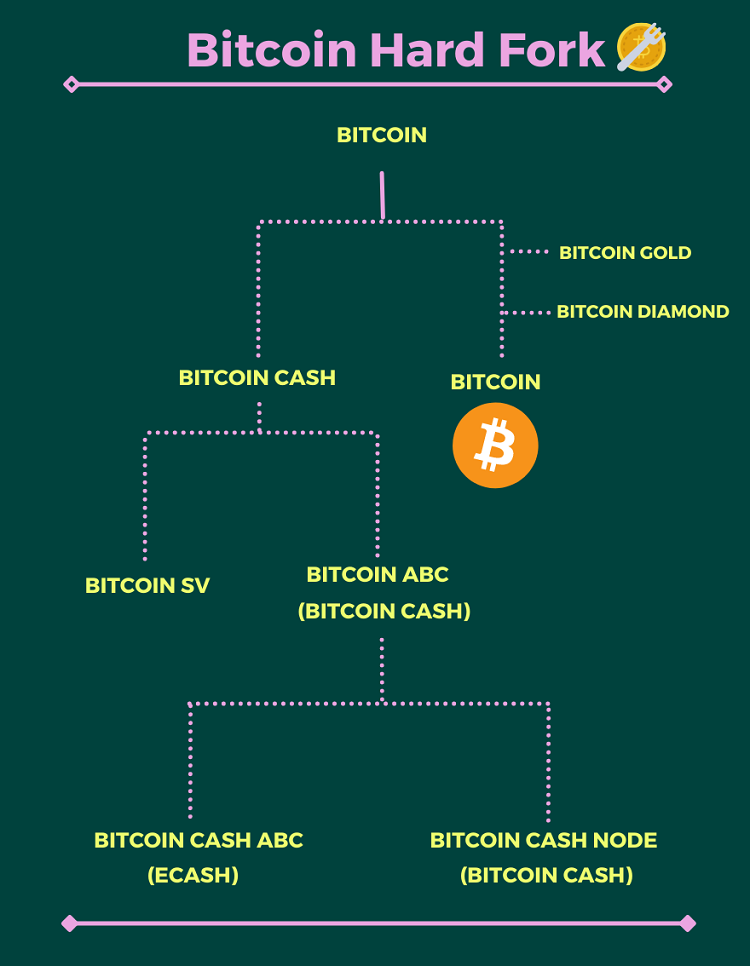
We will introduce you to the most famous Bitcoin Hard Forks that are currently active in the market:
Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
What is a Bitcoin Fork? The most famous name when it comes to Bitcoin Forks is undoubtedly Bitcoin Cash, which was born following a Bitcoin hard fork in 2017.
At that time, Bitcoin still faced limitations as it could only process an average of 7 transactions per second and had high fees. This caused disappointment among many people. They hoped that if Bitcoin were to be used as a global payment system, then it needed to improve its scalability and performance.
This led to a division within the Bitcoin community at the time, splitting into two groups.
- Group A: Believed Bitcoin was slow and the fees too high, wanted Bitcoin to evolve to gradually become a medium of exchange.
- Group B: Wanted Bitcoin to remain as it was, viewing Bitcoin as a store of value similar to gold.
=> Due to the dispute, a Bitcoin hard fork occurred, and those in Camp A created Bitcoin Cash, with the main feature being: increasing the maximum block size from 1MB to 8MB, allowing for faster transaction processing and lower costs.
The figure behind the Bitcoin Cash project is Roger Ver – a well-known cryptocurrency investor, often referred to as “Bitcoin Jesus.” Roger believes that Bitcoin Cash is the “real Bitcoin” and that it will surpass Bitcoin to become the number one cryptocurrency.
♦ Realtime price: $ 335.58 (0.62%)
♦ Market capitalization: $ 6.66 B
♦ Capitalization ranking: 23
Bitcoin SV (BSV)
If Bitcoin Cash is a fork of Bitcoin, then Bitcoin SV is a fork of Bitcoin Cash, making it a second-generation fork.
Over time, the Bitcoin Cash team implemented several changes aimed at enabling smart contracts to run on Bitcoin Cash. However, some in the community disagreed with these changes.
The opposing group argued: By making these changes, Bitcoin Cash was straying from the original vision Satoshi Nakamoto (the founder of Bitcoin) had for Bitcoin, which was to become a medium for transactions.
=> Therefore, in November 2018, a hard fork of Bitcoin Cash occurred, resulting in the creation of two separate blockchains: Bitcoin SV and Bitcoin ABC.
(Note, since Bitcoin ABC received more support, it continued to inherit the price and the chart of Bitcoin Cash and is considered to be Bitcoin Cash).
♦ Realtime price: $ 28.34 (1.35%)
♦ Market capitalization: $ 562.55 M
♦ Capitalization ranking: 125
eCash (XEC)
eCash (XEC) is actually Bitcoin Cash ABC (BCHA), but it was renamed in July 2021 to avoid confusion with other Bitcoin versions.
Bitcoin Cash ABC was also created after a hard fork of Bitcoin Cash. The reason was due to disagreements within the community. Amaury Sechet, a member of the Bitcoin Cash development team, wanted to allocate 8% of the newly mined coins from miners to a development fund under his management. This proposal faced opposition from some members.
=> This led to a hard fork on the Bitcoin Cash blockchain, resulting in Bitcoin Cash Node and Bitcoin ABC.
- Since Bitcoin Cash Node received more support, it continued to be known as Bitcoin Cash.
- Bitcoin Cash ABC represented those who supported Amaury Sechet, and after some time in operation, it was renamed to eCash.
♦ Realtime price: $ 0.00002 (2.30%)
♦ Market capitalization: $ 394.91 M
♦ Capitalization ranking: 160
Bitcoin Gold (BTG)
Bitcoin Gold is a blockchain that was forked from Bitcoin in October 2017. While Bitcoin Cash focused on reducing transaction fees, Bitcoin Gold aimed to make Bitcoin more “decentralized.”
Although Bitcoin’s decentralization is at 100%, the type of decentralization Bitcoin Gold aimed for was about how transactions were verified/mined. The reason for this is because a large portion of mining activities was concentrated in China. Mining pools are where many individuals “pool” their hardware resources together to increase their chances of earning mining rewards.
Bitcoin Gold introduced a new mining process to ensure that expensive, specialized hardware could not improve someone’s chances of earning mining rewards.
An easy example:
If a Ferrari races against a Mini Cooper, which car do you think will win? Obviously, the Ferrari because it has a more powerful engine. However, Bitcoin Gold was created to level the playing field, so when the Ferrari enters the race, it’s just like a Mini Cooper, both have an equal chance of winning.
Like both Bitcoin and other Bitcoin Forks, Bitcoin Gold has a limited supply of 21 million. Its block size is also 1 MB, but instead of taking 10 minutes like Bitcoin, it only takes 2.5 minutes to confirm a transaction, which is four times faster than Bitcoin.
Since its launch, Bitcoin Gold has been functioning really well. However, in May 2018, Bitcoin Gold experienced a very serious “51% attack”. This is when an individual or group of individuals achieves more than 51% of the total hash power of the blockchain, allowing them temporarily to make changes to the network. As a result of this event, over 18 million dollars of BTG were stolen.
=> This incident was a huge irony for Bitcoin Gold. Its purpose was to prevent miners from gaining too much control, yet it fell victim to this very “accident.”
♦ Realtime price: $ 0.611993 (2.51%)
♦ Market capitalization: $ 10.72 M
♦ Capitalization ranking: 1389
Bitcoin Private (BTCP)
Bitcoin Private was launched in March 2018, but BTCP is not a direct fork from Bitcoin; it is a bit more complex.
-
ZCash was forked from the original Bitcoin.
-
ZClassic was forked from ZCash.
-
Bitcoin Private was forked from ZClassic.
The main founder and developer of Bitcoin Private is Rhett Creighton. The idea that Creighton proposed with Bitcoin Private was to combine the privacy features of ZClassic with the security and popularity of Bitcoin. In total, there will be a maximum supply of 21 million BTCP coins. The block size is twice that of Bitcoin at 2MB, and it can also confirm transactions four times faster.
At the time of the fork, anyone holding BTC at the time of the launch was awarded a 1:1 ratio of Bitcoin Private (BTCP). Additionally, anyone holding ZClassic (ZCL) was also entitled to a 1:1 supply. This means that if you were holding both Bitcoin and ZClassic, you would receive Bitcoin Private twice.
♦ Realtime price: $ 14.70 (4.91%)
♦ Market capitalization: $ 1.90 M
♦ Capitalization ranking: 2686
Bitcoin Diamond (BCD)
What is a Bitcoin Fork? Bitcoin Diamond was forked from the original Bitcoin. Its goal is to allow users to be even more anonymous. In this sense, its purpose is very similar to Bitcoin Private.
Bitcoin Diamond was launched in November 2017. While other currencies maintain a total supply of 21 million coins, Bitcoin Diamond has increased this number tenfold. Therefore, if you hold 5 Bitcoins, you would receive 50 BCD.
Bitcoin Diamond improved the block size from 1MB to 8MB. However, Bitcoin Diamond may not have received much trust, and they don’t even have a proper whitepaper. The founders of Bitcoin Diamond are only known as miners, with the names “Team Evey” and “Team 007”.
♦ Realtime price: $ 0.031313 (-4.27%)
♦ Market capitalization: $ 5.89 M
♦ Capitalization ranking: 1755
IN SUMMARY:
-
What is a Bitcoin Fork? A Bitcoin Fork is a modification or upgrade to the Bitcoin blockchain.
-
There are two types of Forks: Bitcoin Hard Fork and Bitcoin Soft Fork.
-
A Hard Fork is a change that results in two parallel blockchains, both old and new.
-
Bitcoin Cash was created with the aim of being faster and cheaper.
-
Bitcoin SV was created to maintain the original purposes of Satoshi’s Vision.
-
Bitcoin Gold was created with the desire to make Bitcoin more decentralized.
-
Bitcoin Private and Bitcoin Diamond were created with the aspiration to make Bitcoin more anonymous.
Related post:
The above are the details about what is Bitcoin Fork, as well as the most prominent Bitcoin Fork versions that invest286.com wants to introduce to you. Hopefully, through this article, you have understood more about Bitcoin and its “siblings” to make wise investment decisions. If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the comments below.



























