If you are a new trader entering the market and want to improve your Forex trading effectiveness, then you should learn about the most important economic indicators in Forex. There are many reports/data released monthly and annually, and they can have a significant impact on market volatility. If you’re not sure which indicators or data are the most important, this article will help you.
Contents
- 1 Top 12 Economic Indicators in Forex
- 1.1 Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) Report
- 1.2 Interest Rates of Central Banks
- 1.3 Inflation Rate
- 1.4 Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- 1.5 Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- 1.6 Producer Price Index (PPI)
- 1.7 Purchasing Managers Index (PMI)
- 1.8 Industrial Production Index (IPI)
- 1.9 Consumer Confidence Index (CCI)
- 1.10 Unemployment Rate
- 1.11 U.S. Retail Sales
- 1.12 Money Supply Data
Top 12 Economic Indicators in Forex
Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) Report
The Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) of the United States is one of the most important economic indicators in Forex that every trader should know. Reasons:
- GDP and employment levels are closely related. Any change in NonFarm data moves very closely with the quarterly GDP changes. Since GDP is released quarterly and NFP is released monthly, NFP data reflects very timely and without delay the current economic situation.
- The NonFarm report has a significant impact on monetary policy. Remember, the FED always cares about two dual goals: price stability and maximum employment. Therefore, Nonfarm data significantly influences market perception and the future of monetary policy in general.
Continuously decreasing Non-Farm Payroll data indicates weakness, and the potential for economic recession. Conversely, if the data shows a continuous increase in employment rate, it may indicate a healthy, growing economy with a low risk of recession.
Nonfarm Release Time: Regularly released on the first Friday of the month, at 7:30 PM (summer time) or 8:30 PM (winter time) Vietnam time.
Data in the Nonfarm Report: A Nonfarm report will include 3 data, which are:

- Non-farm Employment Change: the number of jobs created in the industrial and service sectors in the previous month.
- Unemployment Rate: the percentage of unemployed workers who are still actively looking for a new job in the previous month.
- Average Hourly Earnings: the change in earnings rate in the previous month.
How to Analyze Non-Farm Report:
Non-Farm data has a significant impact on the strength of the USD. In general, when you review this information each month, compare it to both the Previous Index and the Forecast Index. The difference between these three indices will significantly impact investor psychology, causing strong market volatility.
- Actual Data > Forecast: better than expected, in a positive direction (unemployment rate decreases, employment rate increases) will cause USD to strengthen or USD/XXX pairs to Rise, conversely XXX/USD pairs will Fall.
- Actual Data < Forecast: worse than expected, in a negative direction (unemployment rate increases), will affect the USD causing it to weaken, then USD/XXX pairs will Fall, and XXX/USD pairs will Rise.
In general, Forex traders want to see the Non-farm Employment Change increase by at least 100,000 in a given month. This is a sign that the economy continues to grow and it can encourage optimism about the U.S. dollar.
Interest Rates of Central Banks
Another important economic indicator of FOREX is the interest rates of the 8 major central banks around the world, especially the U.S. (usually announced by the FED).
When learning about interest rates, it’s important to consider the monetary policy of that central bank. There are two types:
- Hawkish: means the central bank has tightened monetary policy by increasing interest rates. Investors will move their money from other countries to earn higher interest rates in the country that just increased rates. => This will increase demand for that country’s currency and will increase the value of the currency.
- Dovish: means the central bank has loosened monetary policy by decreasing interest rates. This will cause investors to move their money to other countries to earn higher interest rates. => At this time, the demand for that country’s currency will decrease and the currency will depreciate.
Additionally, you should also pay attention to the actual increase/decrease in interest rates compared to the forecast. If the interest rate is as predicted, the market will fluctuate less, but if there is a large discrepancy, the market will fluctuate greatly.
Inflation Rate
One thing that has a major impact on a country’s currency and its exchange rate is the inflation rate. Inflation is the continuous general price increase of goods and services over time and is the depreciation of a specific currency.
A country with high inflation will see its purchasing power decrease, making domestic goods and services more expensive than the international market. At this time, the domestic currency will be less in demand, while people prefer to use foreign currency. Conversely, when a country has low inflation (or even deflation), the purchasing power of the domestic currency increases. The demand for domestic currency will increase, making its value also rise.
High inflation does not necessarily mean bad for the economy, if it increases moderately, it is a sign that the economy is growing. However, in Forex trading, inflation rates have a significant impact on the exchange rates of currency pairs.
Inflation and interest rates are closely correlated. Many countries try to balance interest rates with inflation rates, but the relationship between these two factors is complex and difficult to manage. Central banks will look at inflation data and then manipulate interest rates to adjust inflation as desired (as the FED has done recently).
- Increasing Inflation ⇒ Depreciating Domestic Currency ⇒ Increase Interest Rates to improve domestic currency value and reduce inflation.
As can be seen, inflation is a “leading” indicator of interest rates and exchange rates. Inflation is likely to have a negative impact on the value and exchange rate of the currency. A low inflation rate does not necessarily mean that the exchange rate of that country is favorable, but high inflation will definitely have a negative impact on the exchange rate of that country.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
GDP stands for Gross Domestic Product and is used to measure the market value of all final goods and services in a country. The GDP index is usually reported periodically by quarter or year.
When there is news of a country’s GDP increasing, it’s good news for that country’s currency. People will want to invest more in this currency, leading to an increase in the value of the nation’s currency.
For example: below about the GBP/USD exchange rate which rose sharply due to the economic report on the m/m GDP of the British Pound (GBP) from 0.0% to 0.3% (while the forecast was just an increase of 0.1%). This exceeded expectations, making the GBP stronger.
The GDP/EUR price chart at the time the news was released:

Consumer Price Index (CPI)
CPI (Consumer Price Index) reflects the relative change in consumer goods prices over time.
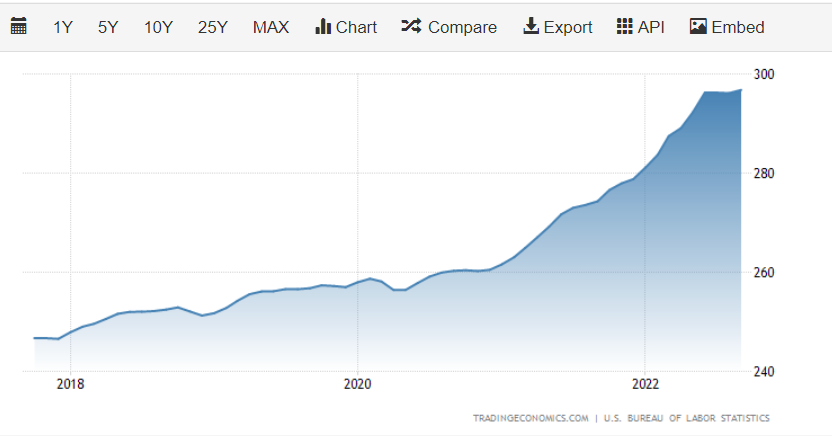
CPI is considered a tool to measure inflation. An increase in CPI means an average price increase and vice versa. Therefore, analyzing CPI has a similar impact on the Forex market as analyzing inflation.
- High CPI can prompt a central bank to increase interest rates in an effort to control inflation trends. When a country’s interest rates are higher, it’s likely that its currency will strengthen as demand for it increases.
- Conversely, a lower CPI may lead to lower interest rates and a decrease in demand for a country’s currency, encouraging consumers to spend, put more money into circulation, and generally stimulate a slow-growing economy.
CPI is an important economic indicator for Forex, having a profound impact on the market. Besides considering the increase/decrease compared to the previous month, investors need to compare actual CPI to the forecasted CPI. For example: if the US CPI rises higher than previously forecasted, it creates a sense that monetary policy will tighten in the near future, leading to a market rise for the US dollar.
Producer Price Index (PPI)
PPI (Producer Price Index) measures inflation in the price of goods from the perspective of producers.
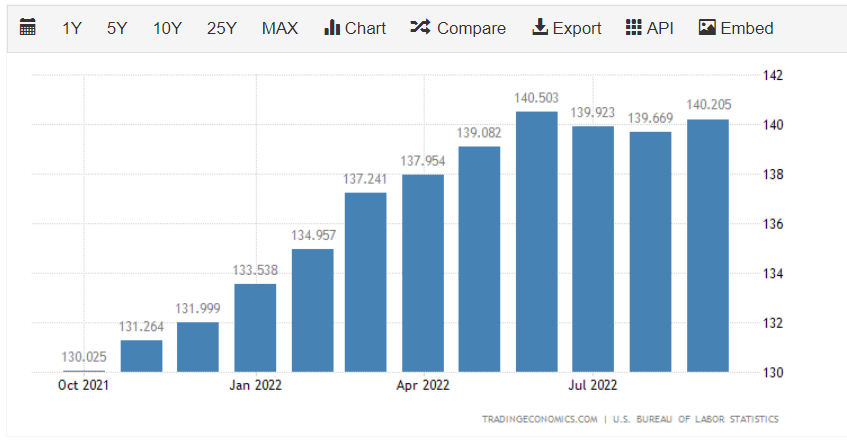
PPI often reflects the trend of the CPI index beforehand, hence, the main significance of PPI in the eyes of investors is the ability to predict CPI. When PPI increases, it’s highly likely that CPI will also increase.
In summary: Actual PPI data higher than forecast should be considered as positive/upward trend for the country’s currency, while actual data lower than forecast should be seen as negative/downward trend.
Purchasing Managers Index (PMI)
The Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) measures the economic health of the manufacturing sector. PMI includes a total of five indices: new orders, inventory levels, production, supplier deliveries, and employment.
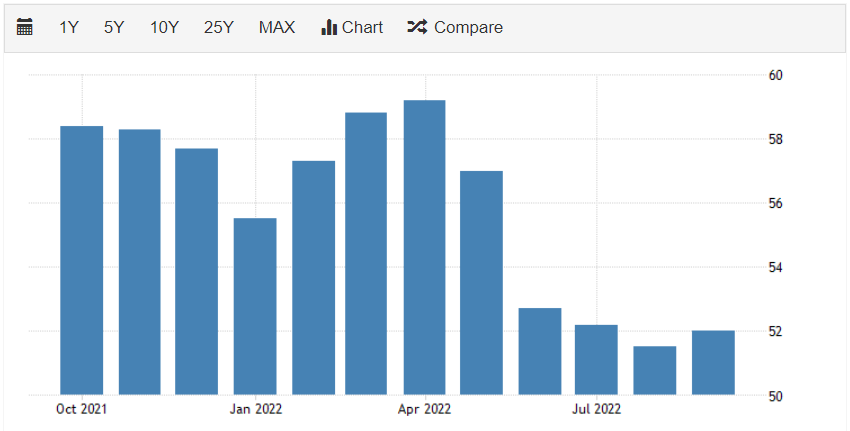
The purpose of PMI: PMI indicates the overall economic condition in both the manufacturing and service sectors. PMI reflects the level of purchasing activity in the manufacturing sector in a month and changes over the months clearly reflect the pace of growth/decline in the service and manufacturing sectors. Additionally, it also helps us anticipate other indices like CPI, GDP… from this, we can gradually guess the position of this economy, whether it meets the expectations of policymakers or not.
In conclusion, PMI is one of the most important economic indicators in Forex, which should be monitored continuously. Rising PMI data indicates a strong economy, leading to the strengthening of that country’s currency.
Industrial Production Index (IPI)
The Industrial Production Index (IPI) is a monthly economic indicator measuring actual output in industries like manufacturing, mining, electricity, and gas. IPI is published mid-month by the Federal Reserve Board (FRB) and reported by the Conference Board.
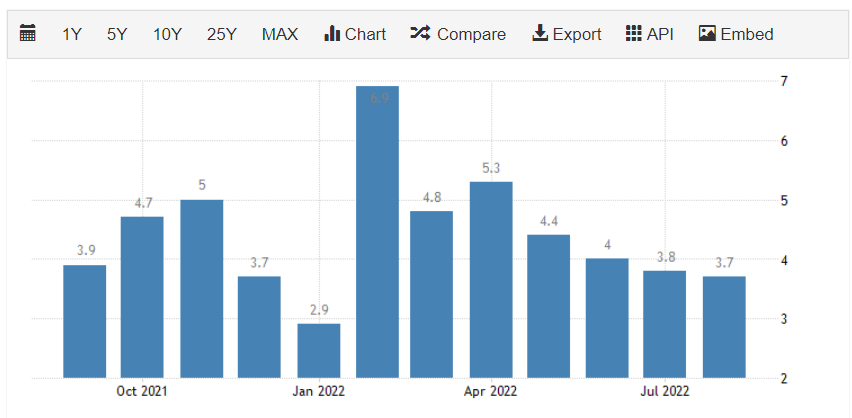
Although manufacturing accounts for only about 20% of the US economy, it is responsible for a significant portion of the US output changes, hence Forex traders must closely monitor it. Additionally, IPI is also correlated with the business cycle, so many analysts use IPI data as an early indicator of GDP.
IPI usually correlates positively with a currency’s value. High IPI indicates improved economic activity in that country, contributing directly to GDP, making that country’s currency appreciate.
Consumer Confidence Index (CCI)
There are two indices in this group: Consumer Sentiment Index (CSI) from the University of Michigan and Consumer Confidence Index (CCI) from the Conference Board.
Both reports are famous and have similar meanings for the Forex market. CCI is published at the end of each month, while CSI is released twice a month. Each month, they survey many US households to understand the optimism about the state of the economy that consumers are showing through their saving and spending activities.
- If they feel secure in their jobs and the current economic times, they are likely to go out and spend more money, thereby promoting economic growth. At this time, CCI is often shown above 100.
- If consumers lack confidence in their jobs and their economic future, they will not go out and spend. This is a sign that the economy is becoming pessimistic. At this time, CCI is often shown below 100.
In summary: If CCI increases, it’s a sign that the economy will grow, and the value of that country’s currency will rise accordingly.
Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate is also one of the most important economic indicators in Forex that needs attention. US unemployment data is released along with the Non-Farm report (discussed in section 1 above).
Unemployment Rate: the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed but actively seeking new employment in the previous month.
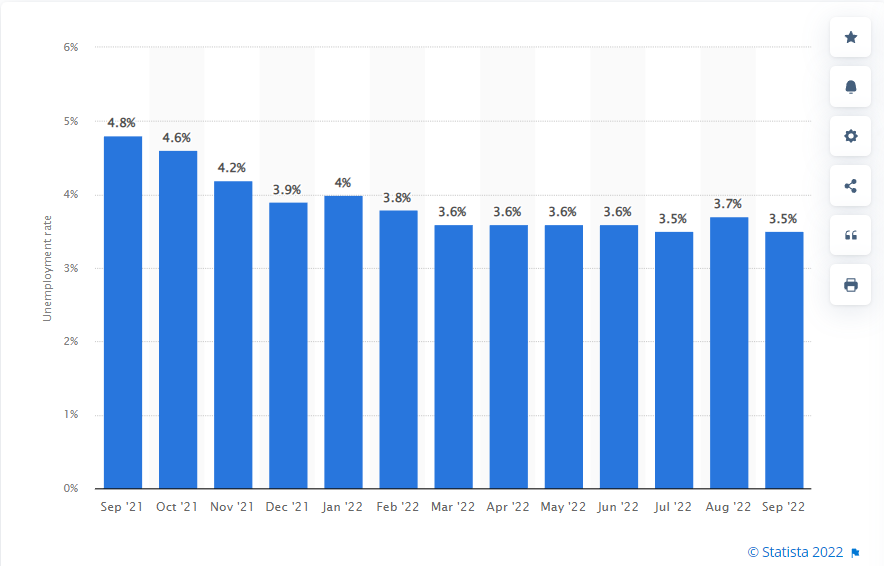
If the economy is recovering but unemployment is increasing, then the unemployment rate acts as a lagging indicator. We often see unemployment continue to rise even after GDP has bottomed out. Unemployment is also closely linked to consumer sentiment (affecting CCI). Extended unemployment periods can severely harm consumer sentiment, and therefore also impact consumer spending and economic growth.
But: If the unemployment rate is 0% or too low, it’s NOT GOOD AT ALL. If no one is unemployed, then in a certain industry needing more labor, business owners will be forced to increase wages to get them to work. Constantly increasing wages may lead to inflation, which is also not good for the economy.
In summary: Evaluating the unemployment rate, a decrease or stability in the unemployment rate is seen as a positive sign for the economy and the currency of that country. However, if the unemployment rate is too low, it is a sign of caution.
U.S. Retail Sales
Retail Sales (RS) are released bi-monthly by the U.S. Census Bureau. They report exactly at 8:30 AM EST in the middle of the month. This data provides an overview of the value of goods sold in the retail trade sector and is an important factor in determining Gross Domestic Product (GDP) – a key indicator of the economy.
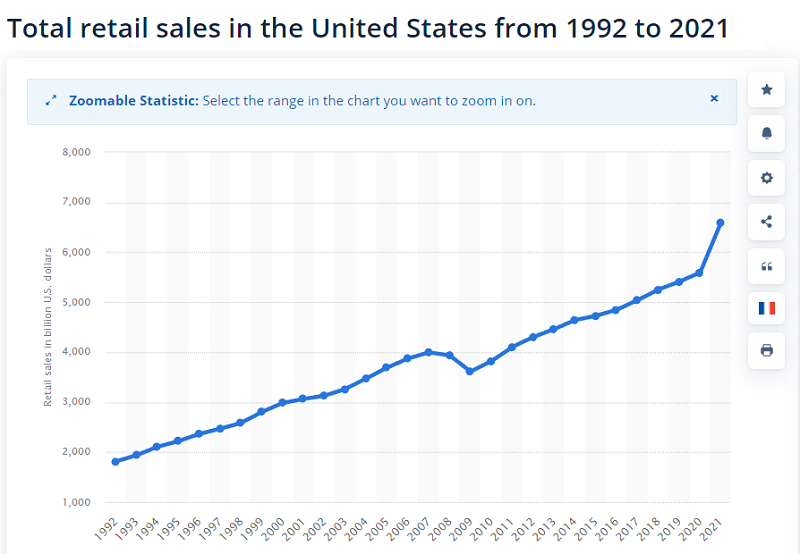
Typically, increasing retail sales indicate the health of an economy and can positively impact the U.S. dollar, but there are also considerations about inflation. Conversely, weak retail sales will negatively impact the market and the U.S. dollar.
Example: In October/November 2020, the RS-Index report from the U.S. Census Bureau showed a modest decline in retail sales, serving as evidence of a stagnant economy. Despite the complexity of evaluating the U.S. economy during the pandemic, disappointing RS-Index information led to a sharp decline in the USD/JPY exchange rate.

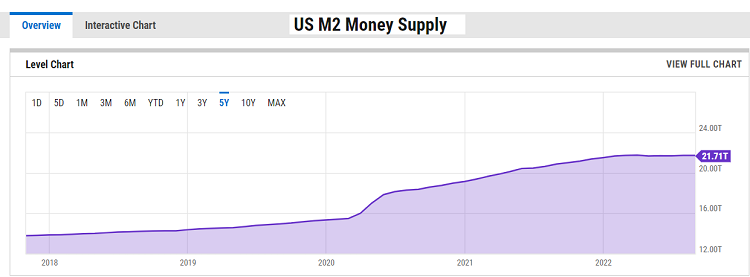
Money Supply Data
Money supply is the total amount of cash in circulation within an economy, divided into:
- Money Supply M1: all circulating cash + demand deposits.
- Money Supply M2: includes M1 + time deposits.
- Money Supply M3: includes M2 + larger, less liquid time deposits, typically financial assets of financial institutions and large corporations.
The most notable impact of money supply is inflation. Inflation is the increase in the price of goods and services over time.
- As the money supply grows, indicating households have more money to spend, total demand increases. Since supply does not change at the same rate as demand, the result is increased prices for goods and services. When inflation rises, central banks will use deflationary monetary policies, such as increasing interest rates. ⇒ Increasing the value of that country’s currency.
- Conversely, a decrease in money supply signals economic recession, job loss, and a shrinking economy. Consistently decreasing money supply will trigger the implementation of expansionary monetary policies, typically future interest rate cuts. This reduces the value of that country’s currency compared to others.
U.S. money supply data is released monthly. You can refer to the data at: https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h6/current/default.htm
In reality, there are hundreds of different economic data released every month for all global economies, and most of them impact exchange rates. However, the above 12 data are the 12 most important economic indicators in Forex that every investor should be aware of. The impact of these economic data can vary in intensity. By monitoring news and economic events, you can grasp monetary policies and predict how exchange rates will fluctuate, thereby diversifying your profits. Wishing you successful trading.



























