What is a smart contract? If you are exploring cryptocurrencies, especially Ethereum or any of its competitors, you will encounter the term “smart contracts” quite frequently. Surprisingly, Smart Contracts even predate cryptocurrencies, having been created in 1994 by a computer scientist named Nick Szabo.
So, what exactly is a Smart Contract (Smart Contract)? How does it work, and how is it applied in the cryptocurrency market? Let’s explore in detail in the following article by invest286.com.
Contents
- 1 Smart Contract – What Is It?
- 1.1 When was the Smart Contract invented?
- 1.2 What is Smart Contract?
- 1.3 How Do Smart Contracts Work?
- 1.4 Examples of Smart Contracts
- 1.5 Advantages and Disadvantages of Smart Contracts
- 1.6 Which Cryptocurrencies Have Smart Contracts?
- 1.7 How are Smart Contracts applied?
- 1.8 What happens if Smart Contracts become popular?
Smart Contract – What Is It?
When was the Smart Contract invented?
Before delving into what a Smart Contract is, let’s first explore who invented it.
In 1994, Nick Szabo (a scientist and cryptographer) came up with the idea of recording contracts in the form of computer code. These contracts would automatically trigger when certain conditions are met, eliminating the need for a third-party intermediary.
Why is that? The answer is simple – because the contracts would execute transactions on a trusted network, entirely controlled by computers. Thus, third-party intervention is unnecessary.
A brilliant idea, isn’t it?
Szabo researched this idea for many years, even writing a book titled “Smart Contracts: Building Blocks for Digital Free Markets”. But the problem was, in 1994, blockchain technology did not exist.
But now, it’s different.
In 2009, Bitcoin first introduced blockchain technology. And in 2015, Ethereum was established and introduced smart contracts running on its blockchain, opening a “new era for smart contract technology operation”.
What is Smart Contract?
I don’t just want you to understand what a Smart Contract is, but also to remember it easily. Therefore, I have tried to avoid as many complex programming terms as possible.
Remember these 3 key points about Smart Contracts:
- First: Smart Contract is an agreement between two people in the form of computer code. They run on a blockchain, so they are stored on a public and immutable database.
- Second: Transactions occurring in a smart contract are processed by the blockchain, meaning they can be sent automatically without a third party.
- Third: Transactions only occur when the conditions in the agreement are met, so there is no need for trust and no fear of being scammed.
Smart Contracts are the foundation behind the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) industry. They are also the basis for the development of decentralized applications (dApps).
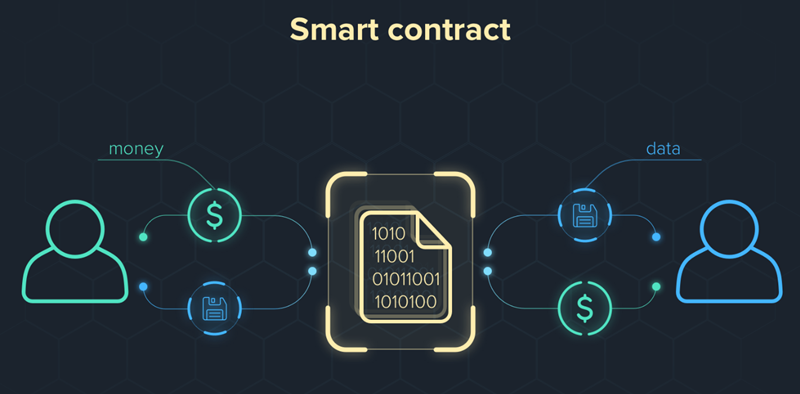
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
How do Smart Contracts work?
As mentioned earlier, it’s all thanks to blockchain.
One great thing about blockchain technology is that as it is a decentralized system, there is no need to pay fees to intermediaries, thus saving time and money. Blockchain is a database shared by many computers (called “nodes”) of different people. Hence, no individual or company can control it.
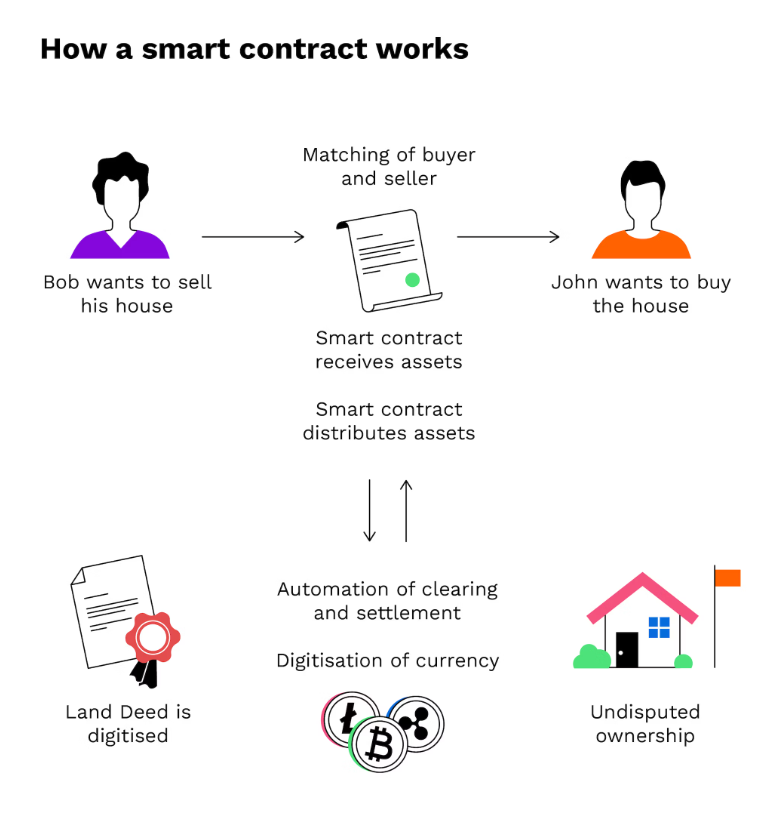
This means that Smart Contracts are nearly impossible to hack. – Hackers would need to attack more than half of the nodes if they want to attack the blockchain or the smart contracts running on it. Therefore, smart contracts can run safely and automatically without anyone being able to change them!
Now, do you understand more about what a Smart Contract is and its advantages?
Smart contracts can be encoded on any blockchain. However, Ethereum is the most popular because it offers unlimited processing capabilities and has the advantage of being a pioneer, so most Smart Contracts today operate on Ethereum’s blockchain.
Examples of Smart Contracts
To help you understand better what a Smart Contract is, we will provide some simple examples for you to visualize.
Case 1: Think of a vending machine (which you may have encountered in many places). You just insert money and choose your item, and the machine delivers your desired product. There is no fear of being scammed, as the machine is programmed with specific conditions. All buying and selling processes happen automatically, without needing a salesperson as an intermediary. => This is the simplest example of a Smart Contract.
Case 2: Imagine Mr. A wants to buy Mr. B’s house, using a Smart Contract on the Ethereum blockchain. It means, this smart contract contains an agreement between A and B, such as:
-
When Mr. A pays Mr. B 300 ETH, he will receive ownership of the house.
These terms have been programmed into a computer, and they cannot be changed. So A will feel very safe when paying B 300 ETH to own the house.
If not using Smart Contracts in this case, A and B would have to pay a lot of fees to third-party companies such as: banks, lawyers, brokerage companies…
Isn’t it great?
No commission fees and time-saving in processing a deal/transaction. This is just one of many examples of smart contracts.
Which Cryptocurrencies Have Smart Contracts?
Which coins can run smart contracts? Most coins with their own blockchain can support Smart Contracts.
Does Bitcoin support Smart Contracts?
Bitcoin has its own blockchain and was the first to exist, so it also allows smart contracts to operate on its blockchain.
However, as it is an early-generation blockchain, Bitcoin’s Smart Contracts are quite limited, only applicable to simple smart contracts, and limited to its currency, such as: payment channels, escrows, multi-signatures, time locks, P2SH…
Over time, many new coins have emerged and have upgraded smart contracts. For example, Ethereum replaced Bitcoin’s limited language with a programming language that allows developers to program their own smart contracts.
Currently, there are many cryptocurrencies capable of creating smart contracts and directly competing with Ethereum, such as EOS, NEO, Cardano…
The Best Cryptocurrencies Supporting Smart Contracts 2025
Smart contracts are one of the reasons why blockchain technology can be so powerful and superior. However, they have only achieved a small part of their potential. If they want to achieve widespread acceptance and transform our daily lives, platforms supporting Smart Contracts need to be faster, safer, more scalable, and more affordable.
Currently, it’s still too early to say which cryptocurrency has the best smart contract functionality. They are all improving daily, so only time will tell. However, based on the above criteria, here are the top 6 cryptocurrencies currently supporting Smart Contracts (according to personal evaluation – not in any specific order):
-
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum was the first cryptocurrency to launch smart contract functionality, so it is the king in this field. According to statistics from State of the dApps, about 80% of DeFi applications run on the Ethereum network.
Unfortunately, due to its success and widespread use by developers, it often gets congested, and gas (transaction) fees get pushed too high. Additionally, Ethereum’s smart contracts do not work well with other blockchains.
(ETH2 may solve this issue, but it’s expected to launch only in 2022).
-
Solana (SOL)
Solana is the fastest cryptocurrency currently, with a speed of 50,000 transactions per second (TPS), while Ethereum only runs at 15 to 45 TPS. Not to mention, Solana’s transaction fee is very low. Solana uses “proof of history” to process transactions quickly.
Currently, Solana has about 400 projects running on its system, including the rapidly growing stablecoin USDC. (USDC runs on both Ethereum and Solana).
-
Polkadot (DOT)
Solana stands out for its speed, but Polkadot stands out for its interoperability (works well with other platforms) – it can be likened to someone who likes to have coffee and chat with everyone around.
Polkadot uses something called parachains. They run parallel to the main blockchain and allow it to process transactions faster. Smart contracts run on parachains, not the main blockchain.
-
Cardano (ADA)
I wouldn’t normally include Cardano in this list, as its ability to support smart contracts only started in September 2021 after the Mainnet Alonzo upgrade, so there hasn’t been enough time to assess its effectiveness.
However, Cardano’s Smart Contracts are worth considering because it is one of the top 5 cryptocurrencies by market capitalization. Cardano has a slow and steady approach to development, so it holds potential.
-
Alogorand (ALGO)
Like other new smart contract platforms, Alogorand has the advantages of low cost, scalability, and speed without compromising security. The person behind the project, MIT professor Silvio Micali, has prioritized making Algorand’s Smart Contract language understandable.
Developers can use various programming languages to write smart contracts on Algorand. One of these, Clarity, is designed to help users easily understand what the contract will do, even if they are not experienced developers.
-
Ergo (ERG)
This Smart Contract platform does not charge a gas fee, making it distinct from other cryptocurrencies in this list. Ergo is designed to handle more complex contracts and has great potential in the Defi sector.
However, it has not yet been listed on many major cryptocurrency exchanges, and its market capitalization ranking is still quite small, so it needs a long and challenging road to build and develop the project.
How are Smart Contracts applied?
The house sale between A & B in the example above is not the only application for Smart Contracts. In fact, smart contracts can be applied to any type of transaction, such as real estate, financial services, insurance, credit authorization, legal processes, and even crowdfunding (ICO).
Applications in Insurance Companies
Atlas Insurance in Malta and Axa in France experimented with Smart Contracts in 2017. They had terms of compensation for airline customers if their flights were delayed.
Example:
-
John is about to fly from NYC to Los Angeles. He sends 5 dollars’ worth of cryptocurrency to Axa’s Smart Contract and provides his flight number. Axa also sends 95 dollars to the same Smart Contract. So, there are 100 dollars in the smart contract.
=> If John’s flight is on time, Axa will receive 100 dollars from the smart contract. But if the flight is delayed, 100 dollars will be compensated to John from the smart contract. Everything is automated.
=> This saves a lot of time and money. Importantly, John does not need to worry about whether AXA will pay him the agreed amount if his flight is delayed. Because John knows that just a delay in the flight will immediately trigger a 100-dollar compensation from the Smart Contract. Fast, no complicated procedures.
Applications in Healthcare Systems
Healthcare systems can also use Smart Contracts to securely store and access patient data.
Example: EncrypGen’s smart contract. This is an application using smart contracts for safe patient data lookup, preventing third-party access.
In this way, patients can control their data. If researchers want to use patient data, they have to pay for it. Moreover, patients have the right to choose whether they want to sell it or not.
Applications for Governments
For governments, Smart Contracts running on blockchains can make the voting system much more reliable and secure.
Example: The application FollowMyVote uses smart contracts and blockchain technology to protect votes from fraud. Each vote, once cast, is recorded in the blockchain and cannot be altered.
This way, voting is always fair, and the winner is always deserving.
Applications in Business
Businesses can benefit greatly from implementing smart contracts. Instead of spending time on payroll and payment procedures for employees, they can use smart contracts.
Example: Company X can set up a Smart Contract with terms that on the 28th of each month, they will pay Mr. Y a salary of 2 ETH.
=> This means Y will always be paid on time and he will never be underpaid. The company benefits as everything is automated, saving them a lot of time and money!
Applications in Cryptocurrency ICOs
Suppose you want to build a project on the Ethereum blockchain. However, to build it, you need a certain amount of money, and the best way is through an ICO (Initial Coin Offering to raise capital).
Step to execute: Create a Smart Contract and its token. Let’s say, the token code is ABC.
=> You want to raise 10,000,000 dollars to start your project and build your application. Imagine 10,000,000 dollars is equivalent to 10,000 Ether. You decide to put 100,000 ABC tokens into the smart contract and each ABC token will have a value of 0.1 ETH.
=> If you sell all 100,000 ABC tokens, you will have the 10,000 Ether you need.
So how does the smart contract work here?
In the smart contract, you will write a term: IF 0.1 ETH is sent to the smart contract, THEN the smart contract will send 1 ABC token to the address that sent 0.1 ETH. That way, the contributors to the ICO always receive the correct amount of ABC tokens.
*** The above are just a few applications of smart contracts in reality.
What happens if Smart Contracts become popular?
From the concept of what a Smart Contract is and its examples in practice as we have described above, you might understand that the essence of smart contracts is to replace intermediaries.
So what would happen if Smart Contracts were widely applied in the future?
Remember the house sale example of Mr. A and Mr. B above? They didn’t need a real estate agent, lawyer, or bank, did they?
=> If smart contracts develop and become popular, perhaps one day we will live in a world without intermediaries.
What will happen next?
The first benefit is that without intermediaries, we will save a lot of money. Moreover, we will no longer need to trust anyone.
However, there is also a potential downside: many people could lose their jobs. Intermediaries are real people, just like you and me. People will not need to hire employees for a job that can be done for free using smart contracts!!!
However, no one knows what the future holds, and it may be a long time before this happens. All we can do is guess and predict, but we must be prepared for all possible outcomes.
After reading the information above, I hope you have a clear understanding of a few things about Smart Contracts:
-
What is Smart Contract? Smart Contracts are similar to conventional contracts. The fundamental difference is that they are digitalized and operate without intermediaries.
-
Some cryptocurrencies can provide smart contract functionalities. The best currently include Ethereum, Solana, Polkadot, Cardano, and Alogorand…
-
Smart Contracts add a lot of value to cryptocurrencies, forming the foundation for Defi applications and Dapps, as well as many other useful applications in life.
-
Smart Contracts can make the world a better place by eliminating fees for intermediaries. They can reduce fraud, delays, and save you a lot of resources.
-
Businesses, governments, and charitable organizations can also benefit from smart contracts. If deployed on a large scale, smart contracts could disrupt many industries, hopefully for the better.
Do you now understand about Smart Contracts – Smart Contracts? If you have any questions or want to argue something, leave a comment to discuss with us. Thank you for reading the article.


























