If you’ve ever transferred coins from one place to another, or simply participated in an ICO, you’ve likely encountered Gas Fees. Gas Fees can be a headache for many, as high gas costs can significantly impact profit margins. But what exactly is a Gas Fee? Why are Gas Fees required for blockchain transactions? Let’s explore the answers in the content below.
Contents
- 1 What is Gas Fee?
- 1.1 What is Gas in blockchain?
- 1.2 What is Gas Fee?
- 1.3 What is the purpose of Gas Fees?
- 1.4 Distinguishing Between Gas Limit and Gas Price
- 1.5 How is the Gas Fee calculated?
- 1.6 How to check Ethereum, BSC gas fees
- 1.7 Gas fees on popular blockchains today
- 1.8 Tips to Reduce Gas Fees (Gas Fee) When Transacting
What is Gas Fee?
What is Gas in blockchain?
Before delving into what a gas fee is, let’s first understand the concept of “gas” in blockchain. Why does “gas” exist in blockchain transactions?
Gas is a unit of measurement for the computational work of transactions running or smart contracts in a blockchain network. This system is similar to using kilowatts (kW) to measure electricity in your home. The electricity you use is not measured in money but instead through kWh per hour.
It’s important to understand that different types of transactions require different amounts of electricity (GAS) to complete.
For example: A simple ETH transfer from one place to another costs 21,000 Gas, while sending ICO tokens from your wallet will consume more Gas due to the higher computational requirements.
What is Gas Fee?
Gas Fee is a type of transaction fee that you will have to pay to execute a transaction. It’s like needing to refuel your motorcycle to keep it running; similarly, in blockchain transactions, you must pay a gas fee for the network system to process the transaction.
In the image below, you will see that executing a transaction involves several computational steps, and each step requires gas to proceed:

For instance, if you want to drive 10km, you need to refuel with 0.5 liters of gasoline and pay 9,000 VND. Similarly, in blockchain, if you want to transfer 1000 ETH to another wallet on the Ethereum network, you must pay a certain amount of gas to carry out the transaction ⇒ This gas amount will be converted into ETH for easy payment.
What is the purpose of Gas Fees?
You might wonder why “GAS fees” are necessary when transaction fees could be based on the amount of assets being traded. Let me explain it simply to you:
Example: The Ether (ETH) cryptocurrency is publicly traded on exchanges, and its market price can fluctuate rapidly. Creating gas units is to separate computational costs in the Ethereum network from the volatile market price of Ethereum because computational costs DO NOT change quickly.
Imagine paying a fixed fee directly proportional to % of Ether (ETH). Suppose its market price is $10, and to transfer 1 ETH, you have to pay 0.5 ETH, then you would only lose $5. But if the price of ETH is $2000, would you want to pay $1000 for this transaction?
That’s why the GAS fee system was created, and it serves several important purposes, such as:
- First: Gas Fees are the fees you need to pay to the blockchain platform when conducting transactions on that platform, more specifically to the validators/miners – the ones who will validate your transaction. Without validators/miners, the network could not exist and operate.
- Second: Gas fees help keep the platform safe and secure. By requiring a fee for each computation performed on the network, developers can prevent bad actors from spamming the network and causing congestion.
- Third: Nowadays blockchains all have their native tokens, and requiring users to pay Gas Fees with the native token helps create price incentives for that token and maintain stability and long-term development of the blockchain.
- Fourth: The Gas fee pricing mechanism ensures that fees are calculated in the most reasonable and fair way. Thus, it prevents the waste of resources on activities of no value to the blockchain network.
Distinguishing Between Gas Limit and Gas Price
To understand Gas Fees better, remember that the structure of Gas Fee will consist of two parts, Gas Limit and Gas Price.
What is Gas Limit?
Gas Limit is the maximum amount of gas you’re willing to spend on a specific transaction. The default value of the Gas Limit varies depending on the time and type of transaction, but you have full control to set the Gas Limit.
Currently in Ethereum, transferring ETH requires a standard 21,000 gas units. But if you execute more complex commands, you will have to pay more than this amount. For example: participating in an ICO requires you to send ETH to its smart contract or when you want to withdraw your ICO tokens to an exchange, the transfer fee is much higher than the default 21,000 gas limit. This is because the smart contracts of an ICO have much more complex codes and require more computation than a simple ETH transfer.
The necessity of the Gas Limit to complete a transaction depends on the complexity of that transaction. The more complex the transaction, the more computing resources it consumes, and therefore, the more gas is used. The gas limit is similar to the fuel tank capacity of a car.
What happens if you specify too little Gas Limit?
Your transaction will initially be processed by the miners, but once the gas runs out, the miners will STOP working on your transaction. The block will record the transaction as “Unsuccessful,” and your ETH will remain in your wallet because there was not enough gas to fully execute the transfer. The gas used for the failed transaction will be kept by the miners for their work, and you WILL NOT get it back. This is what will happen if you specify too little Gas.
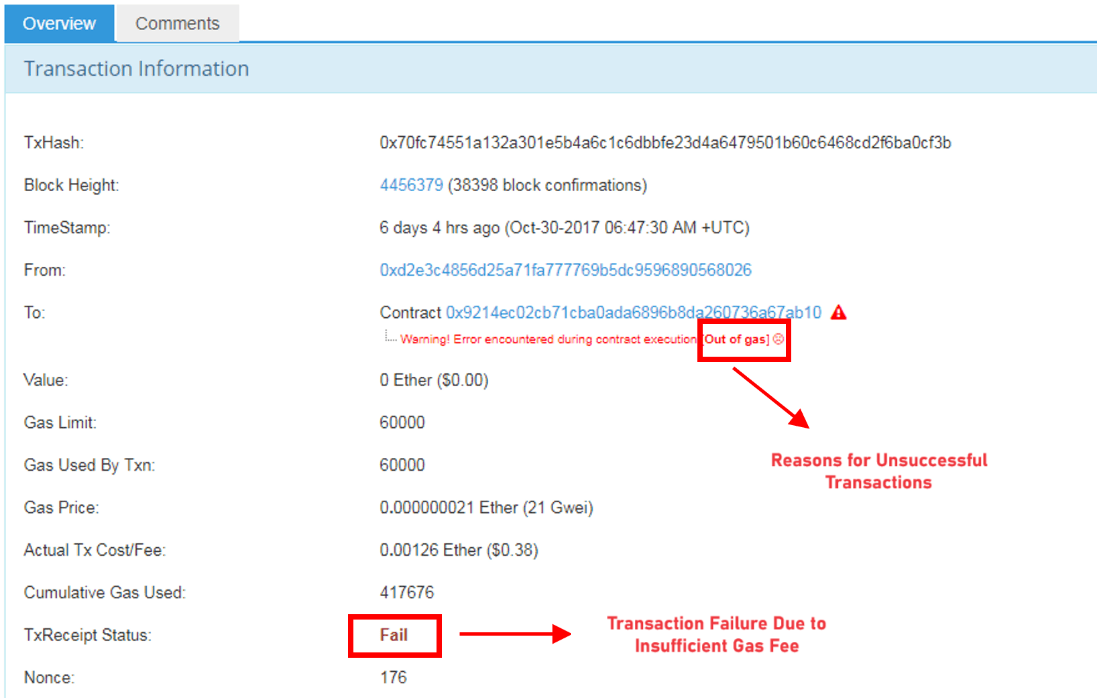
However, you don’t have to worry about setting the Gas Limit value as wallets like Metamask will automatically set the default Gas Limit for the types of transactions you will participate in.
What is Gas Price?
Gas Price, also known as the price of Gas, is the amount of the blockchain’s native coin that users are willing to pay for each unit of Gas. For example: The amount of ETH you’re willing to pay for each unit of Gas when transacting on Ethereum.
Specifically on the Ethereum blockchain, Gas Price is usually measured in Gwei.
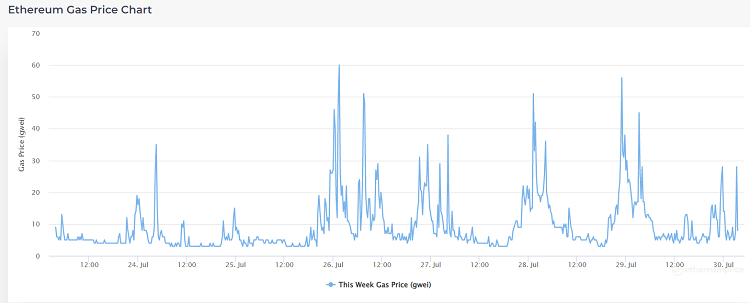
Gwei Gas is a concept that exists only within the Ethereum blockchain. It is a term to denote a very small amount of ETH and is used to pay fees for transactions on the Ethereum network. Each Gwei is equivalent to 0.000000001 ETH (10^-9 ETH). Conversely, 1 ETH represents 1 billion Gwei.
For example: Instead of saying that your Gas Fee is 0.000000001 ETH, you can say that your Gas Fee is 1 Gwei.
To distinguish between Gas Limit and Gas Price, you can think of the example:
Returning to the initial example of making transactions on the blockchain, similar to traveling by car. Here, Gas Limit is the maximum amount of gasoline you want to fill your car with, and Gas Price is the price of each liter/unit of that gasoline.
How is the Gas Fee calculated?
The Gas Fee will be calculated using the following formula:
Gas Fee = Gas Limit x Gas Price
For example: For Ethereum, the Gas Limit requires 21,000 gas units, while Gas Price is priced at 20 Gwei/Gas.
=> Gas Fee = 21,000 × 20 = 420,000 Gwei = 0.00042 ETH.
Therefore, the total gas fee you will have to pay is 420,000 Gwei or 0.00042 ETH.
After the transaction is completed, the unused Gas will be refunded to your account according to the principle: The amount of Gas refunded cannot exceed ½ of the total Gas used in the computation process for the transaction.
How to check Ethereum, BSC gas fees
Gas levels are provided to the Ethereum system to operate stably and fluctuate on each block. You can use the following websites:
- Check overall Gas Fees: https://etherscan.io/gastracker (used to check the average gas fees in the nearest blocks, from there estimate whether the gas fee you are paying is high or low)
- Check detailed Gas Fees: https://ethgasstation.info/index.php (Used to know exactly the level of Gas needed. In addition, it can also calculate the total fees (USD or ETH) to be paid when transferring Tokens based on the provided calculation table).
- Check transaction density: https://ethereumprice.org/gas/ (Because high density often leads to network congestion, high Gas fees, and the risk of transaction failure).
And if you check on BSC, you can check at: https://bscscan.com/gastracker
Gas fees on popular blockchains today
If you understand what Gas Fees are, you’ll know that gas fees on each blockchain are different. Transactions on which Blockchain will pay Gas Fees in the coin of those blockchains. Therefore, depending on the platform, Gas Fees are also calculated in different units (not all platforms use wei like Ethereum).
Remember, to transact on any blockchain, you must own the native coin of that blockchain as Gas. Specifically:
- Transactions on Ethereum: When buying, selling, storing ERC20 tokens like ETH, USDT ERC20,…. ⇒ Pay Gas Fees with Ether (ETH).
- Transactions on Solana: Buying, selling, storing SPL tokens like SRM, RAY,… ⇒ Pay Gas Fees with Solana (SOL).
- Transactions on Binance Smart Chain: Buying, selling, storing BEP20 tokens,… ⇒ Pay Gas Fees with Binance Coin (BNB).
Below is a summary table so you can know exactly which coin to use as Gas Fees:
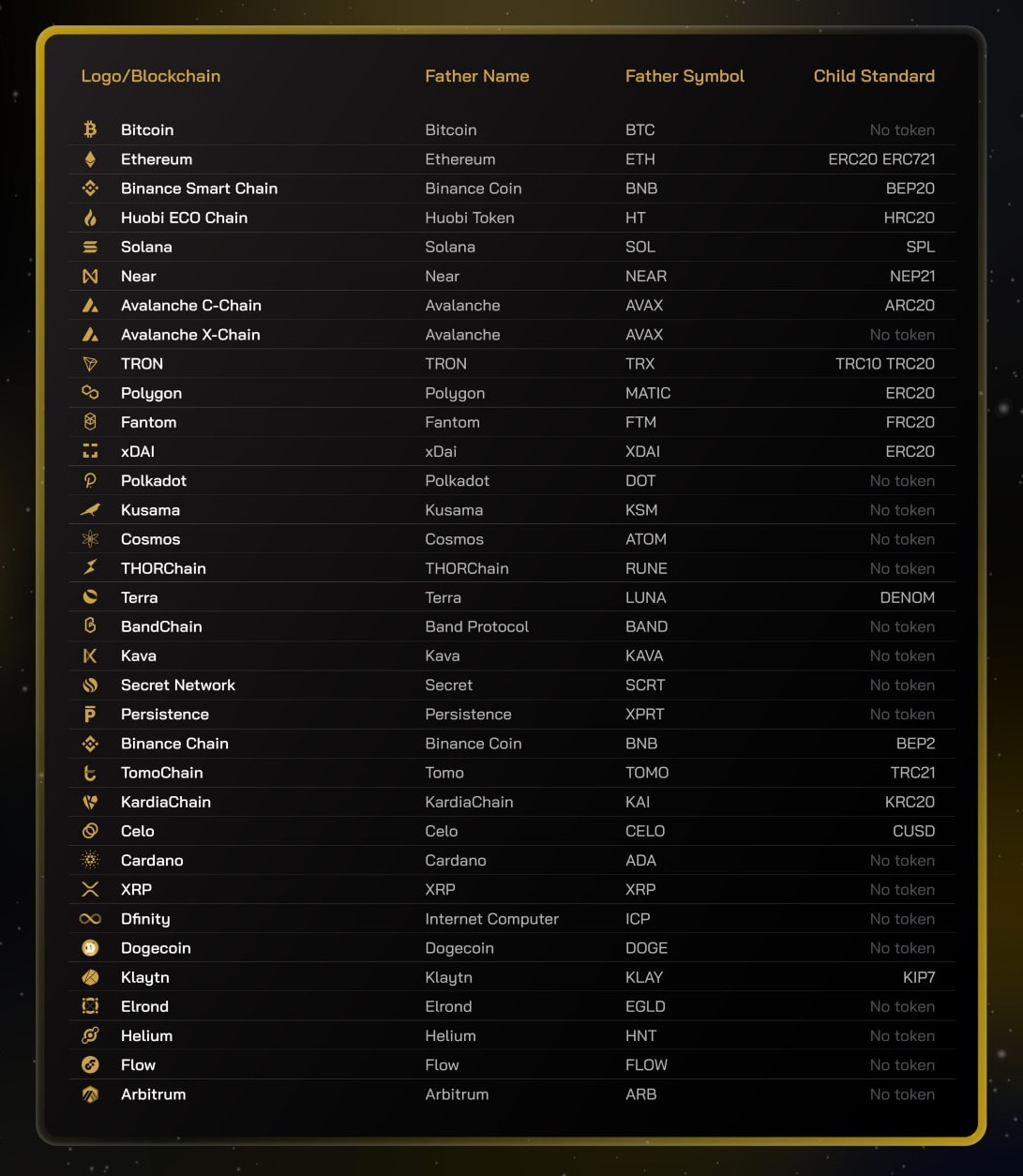
Note:
- Father Token: The coin used as Gas Fee corresponding to the blockchains.
- Child Token: The token standards supported on the corresponding blockchains.
Tips to Reduce Gas Fees (Gas Fee) When Transacting
There are several tips to help you reduce gas fees, they are quite simple and not too complicated, including:
- Check the average gas fee at the time of the transaction: You can check the Blockchain’s average Gas Fee at the links mentioned above. Choosing a Gas Fee below the average can save money, while setting a higher Gas Fee will make your transaction faster.
- Postpone transactions if the gas fee is too high: Gas prices are not the same at any time of the day but will fluctuate according to the network’s transaction demand. Stay away from peak times if you want to save costs.
- Adjust the Gas Limit if necessary: Although adjusting the Gas Limit does not change the gas fee you have to pay. However, if the gas limit is set too high, it could result in an estimated gas fee higher than you can afford to transact. For example, you have 0.01 ETH in your account, but the transaction requires 0.012 ETH because the Gas Limit is up to 500,000. Therefore, you can reduce the gas limit slightly because usually, the transaction will not consume all the initially estimated Gas Limit.
- Do not confuse Gas Price with the amount of ETH you want to transfer: Since Gas Price can be set as much as you like, you could lose a significant amount of money if entered incorrectly. So be extremely careful, always double-check your transactions before hitting the send button, as the blockchain cannot reverse any mistaken transactions.
Above is information about what Gas Fee or Gas Fee is. Understanding Gas Fees as well as how they work is very important when you participate in cryptocurrency investing. Besides, knowing how to save gas fees and use them in the most optimal way will help you a lot in reducing transaction costs and avoiding unnecessary coin loss incidents. If you have any questions, please leave a comment below for us to answer. Thank you for reading the article and wish you success.


























