Currently, Web 3.0 has become a common term in the cryptocurrency field, and many have recognized the need to transition to a decentralized Web 3.0. So, what is Web 3.0, what makes it stand out, and should you invest in it? Let’s delve into the details in the article below.
Contents
What is Web 3.0? Difference Between Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0
You might be interested in:
What Is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is the third generation of the internet, combining technologies from the previous generations (Web 1.0 and Web 2.0) with blockchain technology. Web 3.0 enables websites and applications to process information intelligently, similar to how humans do, through technologies such as machine learning (ML), decentralized ledger technology (DLT), etc.
In simpler terms, in the era of Web 3.0, search engines, social media platforms, markets, and more will be built on the blockchain and supported by cryptocurrencies, creating comprehensive developments in content.

With Web 3.0, data will be interconnected in a decentralized manner (without intermediaries or website owners). Thus, users have more control over their digital content. This is considered a significant leap forward from the current internet (Web 2.0).
Currently, a few Web 3.0 applications have started to emerge. However, it will be necessary to wait until they become widespread and replace the current web infrastructure before we can fully understand their potential.
Differences Between Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0
To better understand what is Web 3.0, let’s explore Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and their differences.
In 1990, when the internet was in its infancy, people did not yet have a definition for Web 1.0, and they simply referred to it as the internet.
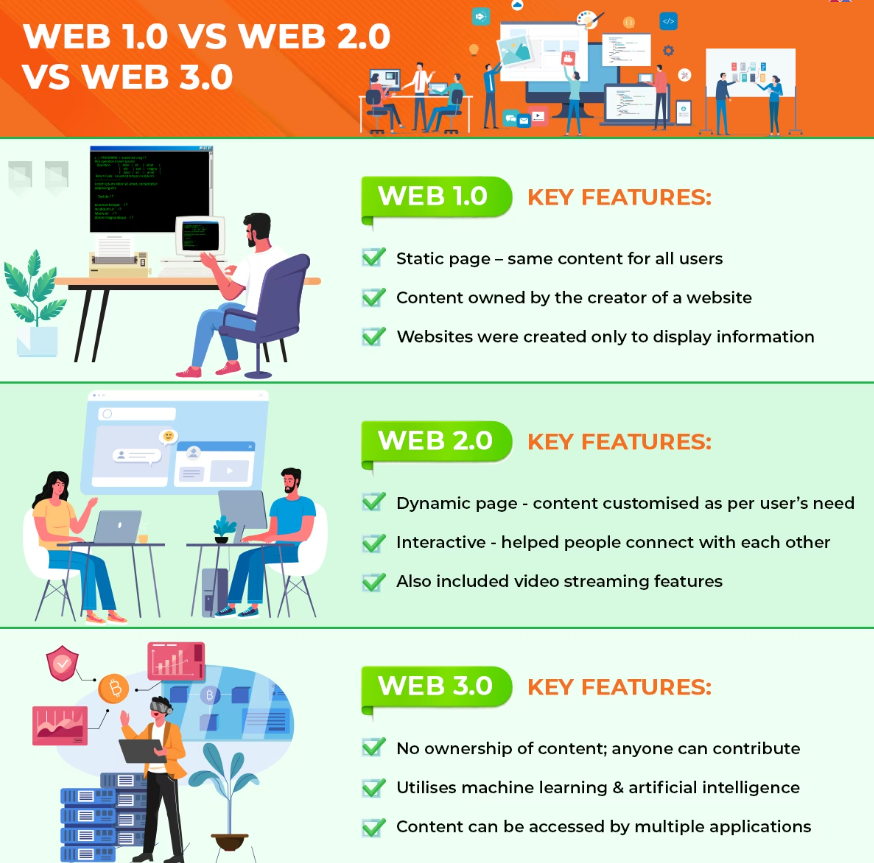
- Web 1.0 Web 1.0 was the first generation of the World Wide Web, spanning from the early 1990s to around 2004. These websites were static, providing one-way content created by businesses, with users like ourselves merely receiving information without much interactivity. Website owners were the ones delivering information, while users could do little else.
- Web 2.0 is the second generation of the World Wide Web, and it is the predominant one we use today. The primary distinction between Web 2.0 and Web 1.0 is the enhanced interaction between users and websites. Web 2.0 witnessed the explosion of social networks, online media, and forums, where users could create content, such as vlogs, blogs, and social media posts. These data were controlled by major corporations like Google or Facebook.

- Web 3.0 represents the latest generation of the World Wide Web, with a focus on decentralization. In contrast to Web 2.0, where content is often managed by centralized entities (e.g., Instagram and Twitter having content moderation authority), Web 3.0 aims to personalize content and grant individuals control over their own data.

Below are some key differences between Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0:
Web 3.0 Applications in Real World
Web 3.0 encompasses four key applications: Blockchain, AI and ML, the Metaverse, and Decentralized Apps (dApps).
- Blockchain Technology: At the forefront, blockchain technology greatly inspires Web 3.0, providing a vital foundation for its functioning.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): These rapidly evolving technologies are crucial for processing vast data sets and enabling predictive analytics.
- The Metaverse: Intersecting with Web 3.0, the Metaverse envisions a future web interface relying heavily on virtual and augmented reality for immersive experiences.
- Decentralized Apps (dApps): Unlike centralized cloud services, dApps offer enhanced data privacy and control, allowing users to collaborate and store data securely.
Risks and Disadvantages of Web 3.0
The lack of centralized gatekeepers in Web 3.0 could pose significant risks to users. Although the decentralized ownership of Web 3.0 is empowering for individuals, the absence of oversight can increase consumer risks, as seen in the collapse of major cryptocurrency exchange FTX.
Decentralization may render regulating Web 3.0 nearly impossible. With the rapid increase of stored online data, unauthorized access to personal data can have devastating consequences.
Emerging cyberattacks present an ongoing challenge. Traditional threats such as phishing and FinTech hacks will remain, while new forms of cybersecurity risks are likely to surface. The potential for widespread data manipulation raises concerns about the spread of misinformation. In a world where anonymity is commonplace, this also applies to malicious entities, complicating the process of holding individuals accountable for cyberattacks and data tampering.
Additionally, the infrastructure of Web 3.0, heavily dependent on blockchain technology, is resource-demanding. Activities like cryptocurrency mining, DeFi transactions, and the decentralization of data consume substantial electricity, thereby exerting pressure on the global energy resources.
A List of WEB3-Based Crypto You Must See
If you already understand what is Web 3.0, you also know that it operates on blockchains, which are what cryptocurrencies provide. That’s why blockchains that can support the operations of Web 3.0 are often referred to as Web 3.0 coins.
Below is a list of the top Web 3.0 coins, ranked by market capitalization:
This is our sharing about Web 3.0. Hopefully, through this article, you’ve gained some understanding of what is Web 3.0 is and which Web 3.0 coins have the potential for investment. It’s evident that Web 3.0 will soon become a trend in the future, so consider investing if you have the opportunity. Wishing you success.


























