If you are interested in or researching the forex and investment markets, you have probably heard of the DXY index. But specifically, what is the DXY index, and how is it calculated? What signals does the DXY index provide in the market? Let’s delve into the detailed answers below.
Contents
- 1 What is the DXY Index (US Dollar Index)?
What is the DXY Index (US Dollar Index)?
What is the DXY index?
The DXY index, also known as the USD Index (with symbols DX, DXY, or USDX), is a measurement of the value of the US dollar’s strength relative to six major currencies from countries that are significant trading partners with the United States. These currencies include the Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Canadian Dollar (CAD), Swedish Krona (SEK), and Swiss Franc (CHF).
The DXY index moves in the same direction as the value of the USD. When the DXY index increases, it indicates that the exchange rates for the USD are rising, and vice versa.
You may wonder, if the DXY index is constructed from six CURRENCIES, how many countries can influence the USD Index?
The answer: 6 CURRENCIES? WRONG. Because this currency basket includes the participation of the EURO (EUR). The EURO is the common currency of the European Union, consisting of 19 countries. Therefore, there are a total of 5 + 19 = 24 countries that can impact the USD Index.
How is the DXY index calculated?
The USD Index is calculated from the exchange rates of six different currencies (accompanied by their weightings in the USD Index), namely:
– EUR 57,6%
– JPY 13,6%
– GBP 11,9%
– CAD 9,1%
– SEK 4,2%
– CHF 3,6%
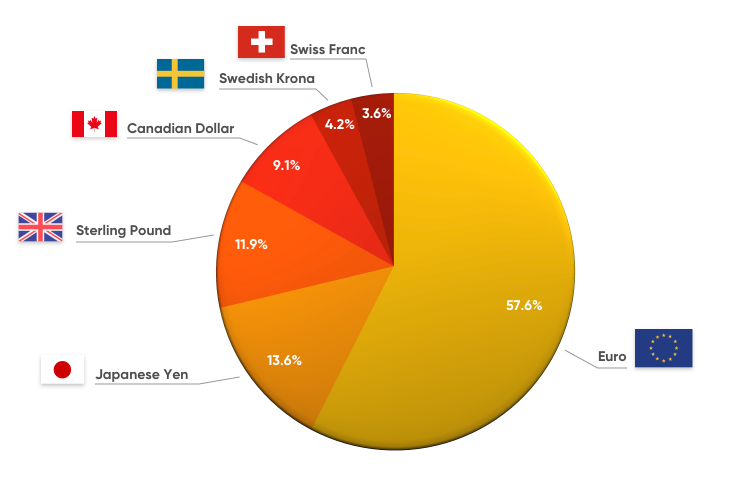
The average weightings are determined as a percentage based on the values above. The weightings differ because each country has different sizes and economies. Hence, their weightings must also differ. The EURO Zone has 19 participating countries, which is why EUR has the largest weighting in the USD Index. Following that is the Japanese Yen since Japan is one of the economic powerhouses.
Specifically, the index is calculated using the following formula:
Looking at the formula and the table above, you can see that the value of each currency is multiplied by its weight. The weight is a positive number when the US dollar is the base currency and a negative number when the US dollar is the counter currency.
Among the six currencies, only the Euro and the British Pound are the two currencies where the US dollar is the base currency. The other four currencies have the US dollar as the counter currency.
History of the DXY Index (US Dollar Index)
You’ve learned what the DXY index is, but you might be curious about where it came from. The US Federal Reserve (FED) created the DXY (US Dollar Index) to monitor the value of the US dollar.
Before the existence of the USD index, the price of gold was always priced at $35 per ounce. However, in 1973, the gold standard was abandoned, and the USD was allowed to float freely in the forex market. Therefore, the DXY index was created to evaluate the strength of this currency. Since 1985, the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE) has managed the USDX, and since then, all transactions related to the USDX (DXY) have been established.
The initial value of the USD Index was set at 100. Subsequent values of the USD Index are calculated relative to this base value. So, if the DXY index = 80, it means its value is only 80% compared to its initial value.
Over its 43-year history, this index has undergone significant changes. On March 5, 1985, it reached its peak at 163.83 – 63.83% higher than its inception. The lowest point for the index occurred on April 22, 2008, at 71.58%, which was 28.42% lower than its establishment.
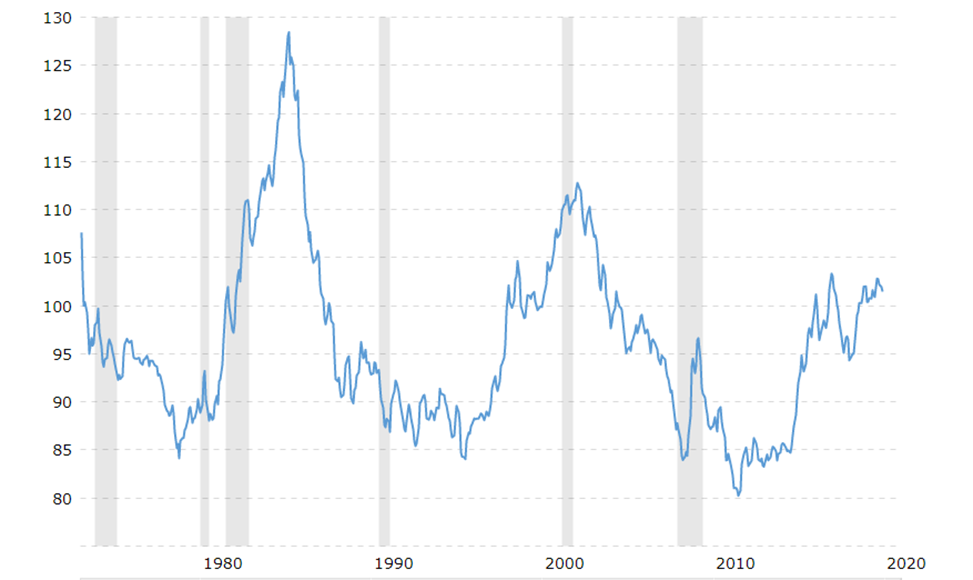
Some notable periods:
- (1): The upward cycle of the DXY index began around 1980, as the global economy emerged from one of the toughest political decades of the 1970s. 1980 also witnessed the peak of gold prices, followed by a decline. Typically, gold and the dollar have an inverse relationship, and the increase in the DXY index became evident around the time gold reached its peak. From 1980 to 1985, the US Dollar Index increased by over 50% as Latin American economies started defaulting on their dollar-denominated debts. As the currencies of Latin American economies collapsed, the US dollar began to rise in value.
- (2): The second significant recovery period for the DXY index started around 1994 when the Fed began raising interest rates. This, coupled with a significant recovery in some technology stocks, caused the USD to appreciate continuously until 2000. However, once again, the upward momentum of the USD disappeared following the dot-com bubble burst and the 9/11 terrorist attacks, which further exacerbated the decline of the US dollar. Until the 2008 financial crisis, the USD Index reached its lowest point in history, and the recession at that time truly spread worldwide.
- (3): This period began around 2011 – 2012, with the DXY index starting to rise again. The USD’s appreciation was due to two main factors. First, in 2011, most Southern European economies fell into severe debt problems. Since all of these economies were part of the Eurozone, they had to be bailed out, leading to the weakening of the Euro and the strengthening of the USD. Second, the Fed first mentioned reducing their bond purchases in 2013 and began raising interest rates in 2015. Then in 2016, President Trump’s trade policies also led to a stronger USD.
- (4): In 2022, the DXY index saw a significant surge. The main reason for this was the record-high inflation in the United States. To curb inflation, the Federal Reserve (FED) raised interest rates. Higher interest rates typically strengthen a currency because when the USD has higher yields, investors start pursuing investments denominated in this currency to earn more, causing a strong demand for USD and driving up its value.
Where to View the DXY Index?
Now that you understand what is the DXY index, the next step is to find a place to access this data. In reality, the DXY index, or the USD Index, is quite popular, so you can easily look it up anywhere. Just like any currency pair, the USD Index has its own chart.
The most common way I usually look up is on Tradingview. Go to the “Chart” section, and then click on the search bar at the top justify corner. Afterward, you can search for the chart by entering “DXY” into the search bar.
Like other indices, looking at the price fluctuations of the DXY index can help determine the current trend of the US dollar. You can indeed use various analytical approaches, such as technical analysis, for DXY analysis when trading in the market.
How to Read the US Dollar Index – DXY?
What is the DXY index? As mentioned earlier, the DXY index is initially set at 100. The subsequent values of the DXY index are calculated using a complex formula (as presented above).
However, you don’t need to remember that formula.
To read the US Dollar Index or DXY, you just need to understand the following information:
- Calculation time: The index is calculated 24 hours a day and 5 days a week, 286 days a year.
- Base value when calculating DXY: 100.00
The DXY index measures changes from the standard level of 100. So, there are two cases: DXY increases or DXY decreases. How to read the DXY index is as follows:
-
When the DXY index increases: If you are looking at the USD Index chart, and you see the value is 103.83, it means that the USD Index has increased by 3.83% since the time the USD Index started being calculated (100.00 -> 103.83).
-
When the DXY index decreases: If you are looking at the USD Index chart, and you see the value is 91.40, it means that the USD Index has decreased by 8.6% since the time the USD Index started being calculated (100.00 -> 91.40).
Take a look at the DXY chart below to better understand this:
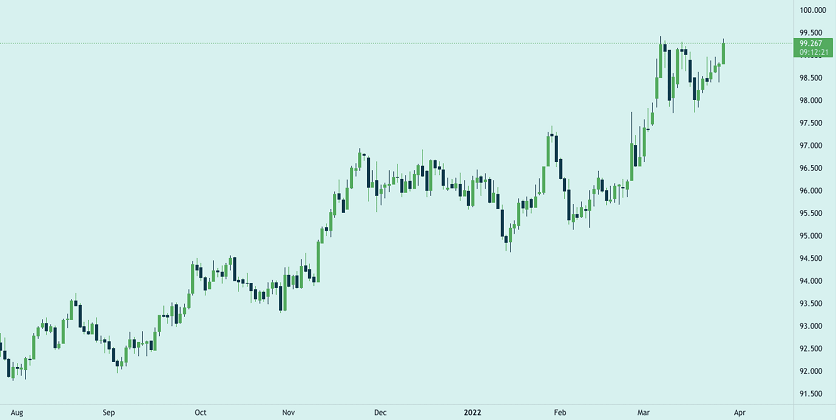
In the image above, you can see that the DXY index today is at 99.267. This means that compared to the standard level of 100, the USD Index has decreased by 0.733%.
Factors Affecting the DXY Index
What is the DXY Index? The DXY index, also known as the US Dollar Index (USD Index), is influenced by the supply and demand of the US dollar and six related currencies.
Therefore, the factors affecting the supply/demand of the currencies in the DXY basket will also affect the DXY index, specifically:
Monetary Policy
For example, in the United States, the Federal Reserve (Fed) implements monetary policies to raise or lower interest rates.
- If the Fed lowers interest rates or takes measures like bond purchases, it encourages investors to borrow money. The dollars borrowed will eventually be spent by consumers and businesses, stimulating the US economy. However, implementing “easy” monetary policies can weaken the US dollar, potentially leading to depreciation. When more money is created, the law of supply and demand comes into play, making the existing money less valuable. Additionally, investors typically seek investments with higher interest rates, so if interest rates decrease, they may move money out of the US and seek higher rates elsewhere, reducing the demand for USD.
- If the Fed raises interest rates: it operates in the opposite direction. Higher interest rates stimulate saving money in banks or increasing demand for the US dollar, causing the value of the USD to rise, and the DXY index also increases.
You can think similarly about the currencies of other countries in this manner.
Inflation Rate
There is an inverse relationship between the inflation rate and the value of a currency. In simple terms, higher inflation erodes the value of money as the cost of goods and services increases.
For example, if commodity prices in the US rise, it reduces the demand for US-made products, and people tend to use more imported goods. At this point, imported goods become more attractive, causing the values of foreign currencies to increase, while the USD loses value. Consequently, this leads to a decrease in the DXY index.
Currency Demand
Regardless of factors like high interest rates or inflation, a country’s currency can remain robust if it’s in high demand. This demand often arises when a country exports goods that are sought after globally, with transactions requiring payment in its currency. Although the United States imports more than it exports, it has cultivated an alternative method to generate sustained demand for the US dollar.
The US dollar’s status as a reserve currency plays a pivotal role. As a reserve currency, it is used internationally to buy key commodities, including oil and gold. When these commodities are priced and traded in US dollars, it fosters a continuous, artificial demand for the currency. This mechanism helps maintain the US dollar’s strength compared to other currencies.
Economic Growth
Strong economies tend to have strong currencies, and weak economies tend to have weak currencies.
- When an economy is growing and thriving, it tends to increase the value of its currency. A strong and growing economy leads to high business profits, increasing the demand for that country’s money, which drives up the value of its currency.
- Economic growth slowing down will lead investors to take their money elsewhere, potentially weakening the currency of that country.
How does the DXY index affect the investment markets?
What is the DXY Index? The US Dollar Index (DXY) tracks the value of the US dollar against a basket of major world currencies. When this index is rising, it means that the US dollar is strengthening relative to the basket, and vice versa.
Therefore, the DXY is a reliable indicator of the USD’s value in the global market. Based on the DXY, investors can make predictions about market trends, thereby making informed investment decisions.
Impact of DXY on the Forex Market
For Forex traders, observing the fluctuations of the DXY index is crucial. The US dollar is the most widely traded currency in the Forex market. Most currency pairs and commodities traded extensively involve the US dollar, such as EUR/USD, USD/CHF, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CAD, and more.
- If the USD is the base currency (the currency on the justify side of the pair’s quotation), then the DXY index and the price of that currency pair are likely to move in the same direction.
- If the USD is the quote currency (the currency on the right side of the pair’s quotation), then the DXY index and that currency pair are likely to move in opposite directions.
(For example, in the USD/EUR currency pair, the euro (EUR) is considered the base currency, while the USD is the quote currency).
When the DXY index shows a clear upward trend, it signals the strength of the US dollar, and traders should look for opportunities to buy USD. Conversely, when the DXY index indicates a downward trend, you should seek opportunities to sell USD.
However, predicting the fluctuations of the DXY index for effective Forex trading is challenging. Therefore, it is essential to combine various skills in technical analysis, support and resistance levels, and more to make the most accurate investment decisions.
Impact of DXY on the Stock Market
The DXY (US Dollar Index) can have several impacts on the stock market:
- Earnings of Export-Oriented Companies: When the DXY strengthens, it typically makes the US dollar stronger relative to other currencies. This can have a positive impact on companies that generate a significant portion of their revenue from exports. A stronger USD can make their products or services more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially leading to reduced demand. Conversely, when the DXY weakens, it can benefit export-oriented companies as their products become more competitively priced in international markets.
- Import Costs: Companies that rely on imported raw materials or goods may face higher costs when the DXY strengthens. A stronger dollar can increase the cost of importing, which can negatively affect profit margins for businesses that heavily depend on imported inputs.
- Multinational Corporations: Large multinational corporations that operate globally can be affected by currency exchange rates. When the DXY strengthens, their overseas earnings in foreign currencies can be worth less when converted back to US dollars, potentially impacting their overall profitability.
- Investor Sentiment: Changes in the DXY can influence investor sentiment. A strengthening DXY might be seen as a sign of confidence in the US economy, which could attract more foreign investment into US stocks. Conversely, a weakening DXY might be viewed as a sign of economic uncertainty, which could lead to capital flight from US markets.
- Interest Rates: The DXY can also influence the monetary policy decisions of the Federal Reserve (the US central bank). A stronger DXY might give the Fed more room to consider raising interest rates, which can impact borrowing costs for companies and consumers. Higher interest rates can potentially dampen economic activity and affect stock market performance.
- Commodities: Some commodities, like oil and gold, are priced in US dollars globally. When the DXY strengthens, the cost of these commodities in other currencies can rise, potentially impacting companies and industries that rely on these commodities as inputs.
- Foreign Investments: A strong DXY can attract foreign investors to US markets, as they can benefit from both potential stock market gains and currency appreciation if the USD strengthens further. This influx of foreign capital can impact stock prices.
It’s important to note that the impact of the DXY on the stock market is not always straightforward and can vary depending on other economic and geopolitical factors. Investors often consider a combination of factors, including interest rates, corporate earnings, and global economic conditions, when making investment decisions in response to DXY movements. Additionally, the degree of impact can vary between different sectors and industries within the stock market.
Impact of DXY on the Cryptocurrency Market
Bitcoin is the leading cryptocurrency in the market, and most altcoins tend to follow its lead. Therefore, it’s important to consider the historical movements of Bitcoin and the USD Index (DXY) as shown in the images below:
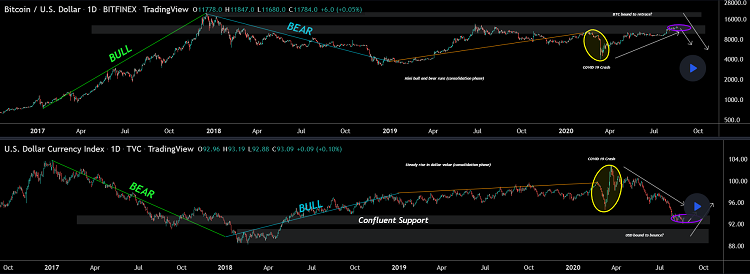
- From 2017 to 2018, we saw Bitcoin’s price rise parabolically, while the US dollar weakened.
- From 2018 to 2020, Bitcoin experienced price cycles of both declines and minor gains, while the USD Index remained stable.
- The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 led to a rapid increase in the USD, while the price of Bitcoin experienced significant declines.
- From early 2022 to the 10/2023, the value of the USD has risen sharply, with the DXY index surpassing its highest level in 20 years, while Bitcoin has maintained a downward trend.
=> It can be observed that Bitcoin and the USD Index typically move in opposite directions. This suggests that Bitcoin was created as a hedge against USD inflation.
- When the USD weakens (high inflation), the demand for Bitcoin tends to increase, and vice versa.
- When the USD strengthens, many people may want to sell Bitcoin for USD..
Impact of DXY on the Gold Market
Gold and the USD are considered global currencies. Many foreign banks hold the USD as a reserve currency or invest more in gold to protect their assets in times of economic volatility.
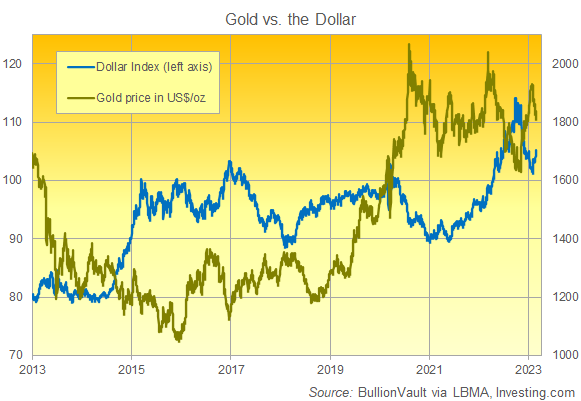
- When the USD weakens, banks and investors worldwide tend to buy more gold to protect their wealth and guard against the depreciation of the US dollar.
- When the USD strengthens, more investors and banks may opt to sell gold for USD, reducing the demand for gold and potentially causing its value to decline.
=> The Gold market typically moves inversely to the DXY (USD Index).
However, the correlation between gold prices and the DXY is not always clear-cut, as there are many external factors that also influence gold prices. For example, during times of conflict, some may buy more gold to preserve value, while others may consider holding USD as a safer option. Therefore, the impact of the DXY on gold prices can vary depending on the specific market conditions and contexts.
- What is the DXY Index? It is an index that measures the strength of the USD against six major currencies.
- The currencies in the DXY basket include: Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Canadian Dollar (CAD), Swedish Krona (SEK), Swiss Franc (CHF).
- The DXY index also has several other names: the US Dollar Index, the USD Index, or it can be symbolized as DX, USDX.
- The DXY index will move in the same direction as the value of the US dollar. When the DXY increases, the value of the US dollar is also increasing, and vice versa.
- The DXY index was created by the Federal Reserve of the United States (FED) in 1973, with an initial base score of 100. For example, if the DXY index is 103, it indicates that the value of the US dollar has increased by 3% since its base year of 1973.
- You can look up the DXY index on Tradingview or many other chart research websites by typing ‘DXY.’
- Factors influencing the DXY include interest rates, inflation, demand for money, and the level of economic growth.
- The DXY index often has a certain correlation with the stock market, cryptocurrencies, gold, and is a crucial signal in Forex trading.
The above are our insights into what the is DXY index, how to calculate the DXY index, and analyze the impact of the DXY index – the strength of the US dollar on some investment markets. We hope that through this article, you have gained an understanding of the DXY (USD Index) to apply it to analysis and make informed investment decisions. If you have any further questions, please leave them in the comments section. Thank you for reading, and we wish you successful investments.



























